
Like the thickness of the troposphere as a whole, the depth of the boundary layer is usually greatest in the tropics and least near the poles. The depth of the boundary layer also tends to vary with latitude. A boundary layer is the layer of fluid in the immediate vicinity of a bounding surface where the effects of viscosity are significant. The boundary layer typically extends upward about 200 to 500 meters (650 to 1,640 feet), but can be as thin as 50 meters (164 feet) or as deep as 2 km (6,562 feet). The boundary layer is quite thin over smooth water or ice, and much thicker over hilly, tree-covered, or urban terrains with many large buildings. The boundary layer is defined as that part of the atmosphere that directly feels the effect of the earths surface.

A range of velocities exists across the boundary layer from maximum to zero, provided the fluid is in contact with the surface. The fluid in the boundary layer is subjected to shearing forces. As you might expect, different surfaces have more or less influence on wind flow, so the thickness of this boundary layer varies. boundary layer, in fluid mechanics, thin layer of a flowing gas or liquid in contact with a surface such as that of an airplane wing or of the inside of a pipe. Similarly, as a velocity boundary layer develops when fluid flows over a surface, a thermal boundary layer must develop if the bulk temperature and surface temperature differ. Higher up, above the boundary layer, wind speed is much less affected by the details of the surface below. The boundary layer is the region in which flow adjusts from zero velocity at the wall to a maximum in the mainstream of the flow. In fluid dynamics, the boundary layer is the region in which flow adjusts from zero velocity at the wall to a maximum in the mainstream of the flow. Near the surface, the texture of the ground has a strong influence on the movement of winds.

The lowest part of the troposphere, closest to Earth's surface, is called the "boundary layer" (or planetary boundary layer or atmospheric boundary layer). At the same time, since a turbulent boundary layer is much better at resisting flow separation than a laminar boundary layer, tripping the boundary layer can be used to improve stability & control at high angle of attack at the expense of increased skin-friction drag.The Troposphere Atmospheric Boundary Layer That's why wing surfaces must be made flush and smooth. Since turbulent boundary layer has higher skin-friction drag than a laminar one of the same Reynolds number, unintentional boundary layer tripping is undesired. It is attached spanwise along the surface of the wing (facing flat against the surface) at the desired chord-wise location where the laminar-turbulent transition is to take place: Friction between the body and the surrounding air holds back the flow. The following is an example of a turbulator tape. A tin layer of static to slow moving air adjacent to the surfaces of a moving body. At the point of boundary layer tripping, the surface protrusion destabilizes the laminar boundary layer and causes the transition to occur earlier than via natural Tollmien-Schlichting instability. The boundary layer theory will be introduced in this section through a discussion of the characteristics of flow past a flat plate. The atmospheric boundary layer is typically 1 km deep during the day and 100 m deep. In particular, the boundary layer is important for predicting a range of parameters such as.
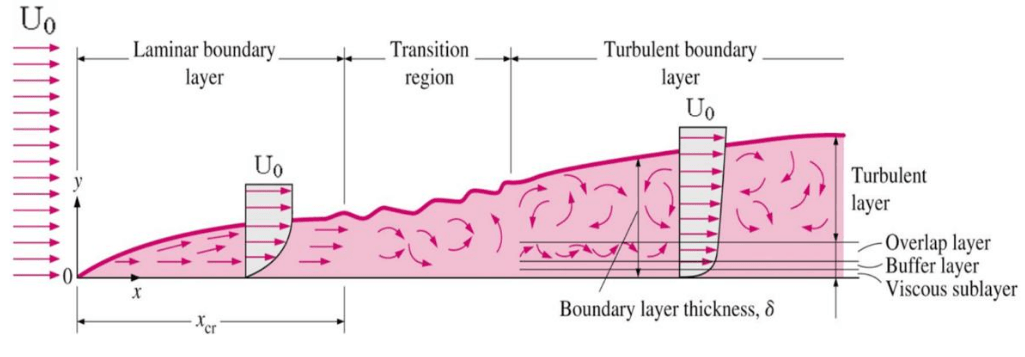
Here prediction and understanding of the local environment requires an understanding of the boundary layer. It is also called the planetary boundary layer or just the boundary layer. The boundary layer is of particular significance to human activities and natural processes occurring on the Earth’s surface. It can happen intentionally (via turbulator) or unintentionally (via imperfect aero-smoothness, such as rivets, bolts, counter-sinks). The atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) is the tropospheric layer that is directly influenced by the presence of Earth’s surface and responds to surface forcings in an hour or less. For the earth, this layer is considered to be roughly the lowest one or two kilometers. Boundary layers are regions of flow near surfaces that experience significant friction forces due to viscous effects.
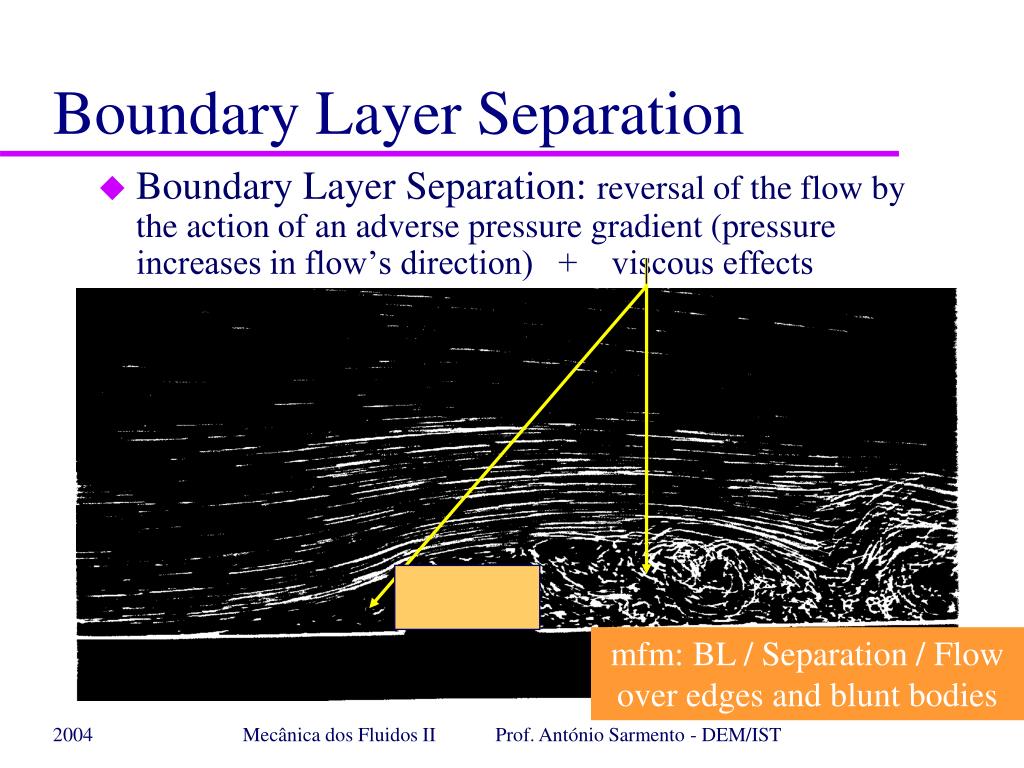
Specifically, the term most often refers to the planetary boundary layer, which is the layer within which the effects of friction are significant. Tripping the boundary layer refers to the action of artificially transitioning a laminar boundary layer into a turbulent one. Atmospheric Boundary Layer Same as Boundary Layer - in general, a layer of air adjacent to a bounding surface.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
